OVERVIEW
Given a document, the nominal compound chain extraction (NCCE) task aims to extract all nominal phrases that are lengthy nominal compounds, and to cluster nominal compounds that describe the same topic or mentions in detail.
For example, in the figure below, there are two nominal compound chains:
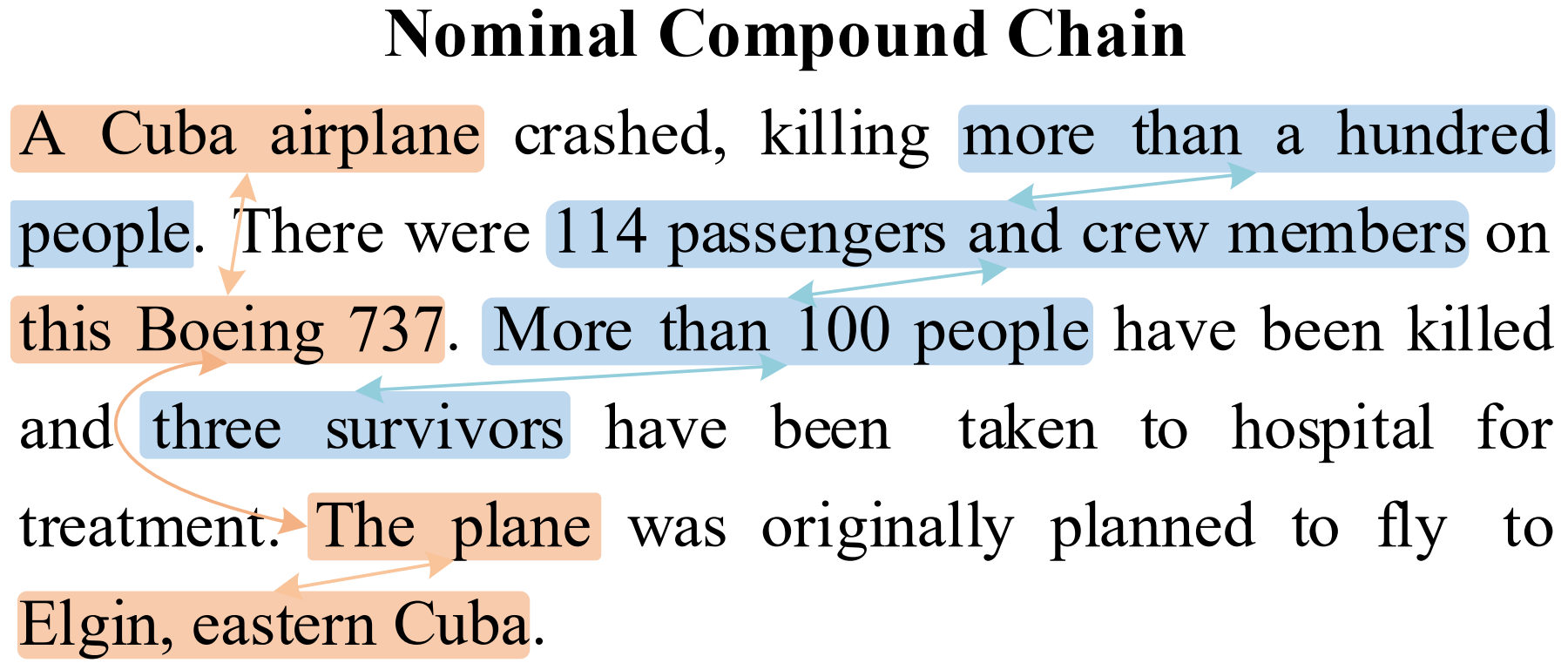
INSTRUCTIONS
Data Source
We manually annotated a high-quality Chinese dataset for facilitating the task. Specifically, the data is built upon Chinese news corpus4. The dataset is annotated based on crowdsource, and then is proofread by language experts in Chinese, by which we can ensure the high consistency on labels, and guarantee the data quality. The final data contains 2,450 documents and 26,760 nominal compounds for a total of 5,096 chains. We randomly split the total data into training, development and test sets with 2,050, 200, 200 documents, respectively. Table 1 shows the statistics of the dataset
Table 1 Dataset Statistics
| Training | Development | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Document | 2,050 | 200 | 200 |
| Compound Chain | 22,565 | 2,124 | 2,071 |
| Max. chain size | 27 | 22 | 19 |
| Avg. compound length | 6.04 | 6.03 | 6.10 |
| Median. compound length | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Max. compound length | 153 | 83 | 78 |
Corpus Sample
A document featuring an annotated nominal compound chain is presented below. The term 'text' denotes the sentence, and within each 'event chain', there may be several 'event terms'. Each event includes a trigger and an entity, where the entity is the nominal compound that we aim to detect.
Additionally, a 'chain_index' term is used to denote the index of each chain. Entities with the same chain index belong to the same nominal compound chain.
For example, in the document below, there are several nominal compound chains:
The start and end indices of each item are the global indices within the document.
Task and Evaluation
Our goal is to extract all nominal compounds and nominal compound chains within the document.
Task Formulation:
Input: Document
Output: Nominal Compound Chains
We primarily evaluate performance based on the extraction of nominal compound chains. Since the task format of NCCE (Nominal Compound Chain Extraction) is similar to coreference resolution, we utilize the evaluation metrics from coreference resolution to assess the performance of models on NCCE. The metrics include MUC(F1), B3(F1), and CEAFφ4(F1).
The average F1 score, Avg.F1, is calculated as follows:
Avg.F1 = (MUC(F1) + B3(F1) + CEAFφ4(F1)) / 3
We use the average of these three metrics as the final score. For more details regarding the evaluation metrics, please refer to this paper: End-to-end Neural Coreference Resolution.
ORGANIZERS
Bobo Li
Language and Cognition Computing Laboratory, Wuhan University
NeXT++ Research Center, National University of Singapore